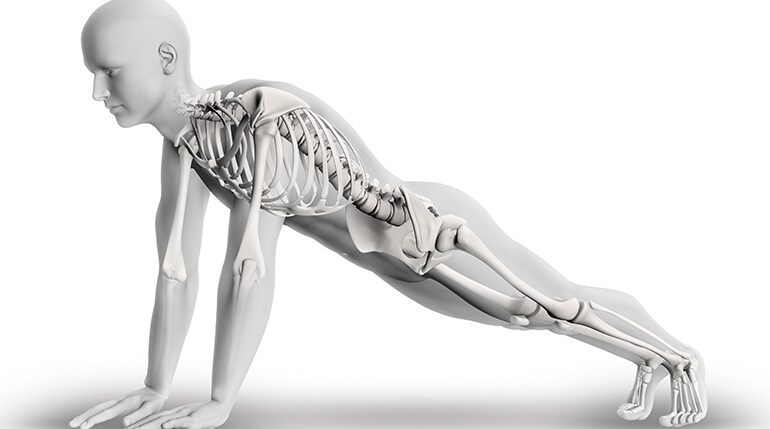

Before beginning any exercise regime, it is essential for one to understand the human body functions and how various muscles respond to certain workouts. A well-coordinated system of bones, muscles, tendons, ligaments and nerves in the human body help us perform complex actions such as running, jumping and walking. Some of the human body systems directly affected by exercise are the skeletal, muscular, cardiovascular, respiratory, nervous and the endocrine system. So let’s dive deeper into how the body benefits from exercise.
The Skeletal System
The human skeleton is made up of 206 bones that hold the body upright, protect the organs and allow movement. When bones join together, they form joints. While some joints, like the one in the skull are joined by the fibrous tissue and are immovable, other joints, such as the vertebrae in the spine are only partially movable and are connected by cartilage. Most of the joints in the human body are freely movable and are called synovial joints. These joints are lubricated by a fluid called the synovial fluid which helps the body absorb shocks caused by high-impact movements like high-intensity workouts and high-pace runs. The ends of the synovial joints are coated with smooth cartilage that provides a certain cushioning which makes it easier for the joints to move without discomfort. Skeletal muscles provide power which allows movement to occur.

Muscular System
The alternate contracting and relaxing of muscles enables movement in the human body. All muscle fibers are connected to nerves that carry messages to and from the brain, and blood vessels that carry oxygen to the muscles and carbon dioxide away. Three types of muscles in the body are:
- The Cardiac Muscle (The Heart Muscle)
- Smooth Muscle (In the Intestines)
- Skeletal Muscles (attached to the Bones)
The cardiac muscle pumps blood to the body thus determining the body’s cardiovascular fitness levels. Smooth muscles are involuntary muscles found in hollow organs such as the stomach, intestines, uterus and bladder. The primary function of the smooth muscle is to perform tasks such as the sealing of orifices or the transport of chyme through contractions of the intestines. However, it is the skeletal muscle that is responsible for every external movement made by the body. The muscle gives shape to the body by holding it upright, stabilizes the joints and enables movement in the bones. While the cardiac and smooth muscles are involuntary, the skeletal muscle is voluntary which means that it’s movements can be controlled by an individual. There are over 600 skeletal muscles in the human body which vary in size. With regular movement and exercise, one will notice the contractions of the skeletal muscles gradually increasing thus increasing the strength, endurance and flexibility of the body.
The Cardiovascular System
The Cardiovascular System consists of the heart, blood vessels and approximately five liters of blood that is transported by the blood vessels. The system is powered by the heart which is the strongest muscle in the human body. It pumps 5 liters of blood through the body, providing oxygen to the organs and blood vessels. On an average, the heart beats a total of 1,00,000 times per day. The walls of the heart comprise of cardiac muscles which are immensely powerful and enable the heart to contract and relax, thus enabling it to pump oxygen-rich blood to the body. Like any other muscle, the heart needs regular physical exercise too.
The Respiratory System
One of the main functions of the Respiratory System is to supply Oxygen to the body while also expelling Carbon dioxide. When we breathe in, the oxygen we inhale makes its way to the lungs from where it travels to the heart which then pumps the it to all the organs of the body. Carbon dioxide is pumped from the body to the heart and then to the lungs which expel it when we breathe out. Hence, deep breathing is recommended as oxygen taken in provides the muscles with higher levels of oxygen which in turn leads to the enhancement of activity levels.
The Nervous System
The nervous system is made up of the brain and the spinal cord And nerves that branch out from the spinal cord to the rest of the body. The nervous system has two parts:
Sympathetic Nervous System
The Sympathetic Nervous System prepares the body for the emergency fight or flight response By increasing the heart rate, Blood pressure and sending blood to the muscles to prepare it for flight. The sympathetic nervous system is dominant mainly when an individual is highly stressed or active.
The Parasympathetic Nervous System
The Parasympathetic Nervous System also known as the “rest and digest” nervous system helps the body calm down by keeping the heart rate, blood pressure and breathing in check. This part of the nervous system focuses mainly on the vital functions such as digestion. It is dominant when the body is in a state of rest. An overstimulation of parts of the nervous system can trigger an imbalance within the body.
Regular exercise however can help balance both the parts of the nervous system. Vigorous activities such as running or brisk walking can help balance the sympathetic nervous system whereas calming activities such as yoga can help balance the parasympathetic nervous system by activating a response of relaxation in the body.
The Endocrine System
The primary function of the Endocrine System is to maintain a balance in the body. This is done by a hormonal release from various organs and tissues in the body that help regulate mood, fertility, energy and metabolism. While human body levels can go out of whack due to hormonal changes, stress and anxiety, pushing in a daily workout can help the body create a balance. Physical activity triggers the body to release “feel good” chemicals such as Serotonin and Dopamine, and Endorphins which help overcome stress and anxiety. Since the natural level of hormones tends to reduce with age, exercise helps the body create a balance to help cope.

The Spine
The spine is made up of vertebrae which are a series of bones connected by disks and ligaments that provide cushioning to the spine, thus protecting the it from damage.
Some of the main functions of the spine are:
- Helping the body stay upright by providing support
- Enabling upper body movement
- Protecting the spinal cord
- Acting as a shock absorber to help prevent damage to the body
The four main sections of the spine, the cervical area, thoracic spine, the lumbar, and the sacrum and coccyx, give it an “S” shaped curve. Since these sections help the spine absorb any shock that may occur, regular fitness activity is essential to keep the spine upright and strong.
Do not miss a single article!
Submit your email id to get new articles directly into your email inbox!
- Employee Wellness Programs: They Really Work! - October 21, 2022
- Yoga Teacher Training Standards - November 18, 2021
- Why You Will Never Go Hungry Again - October 25, 2021




Add Review